Anatomy and Physiology of Skin
Human skin is the first line of defence against infection. It helps to regulate fluid balance and temperature. For the average adult, skin is the largest organ in the human body, covering approximately 3,000 square inches and weighing about six pounds. Skin is made up of three layers. Click on the images below to learn more about each.
(Bak, 2019)
Anatomy and Physiology of Wounds
Wounds are not always caused by surgery. They can be classified into three types:
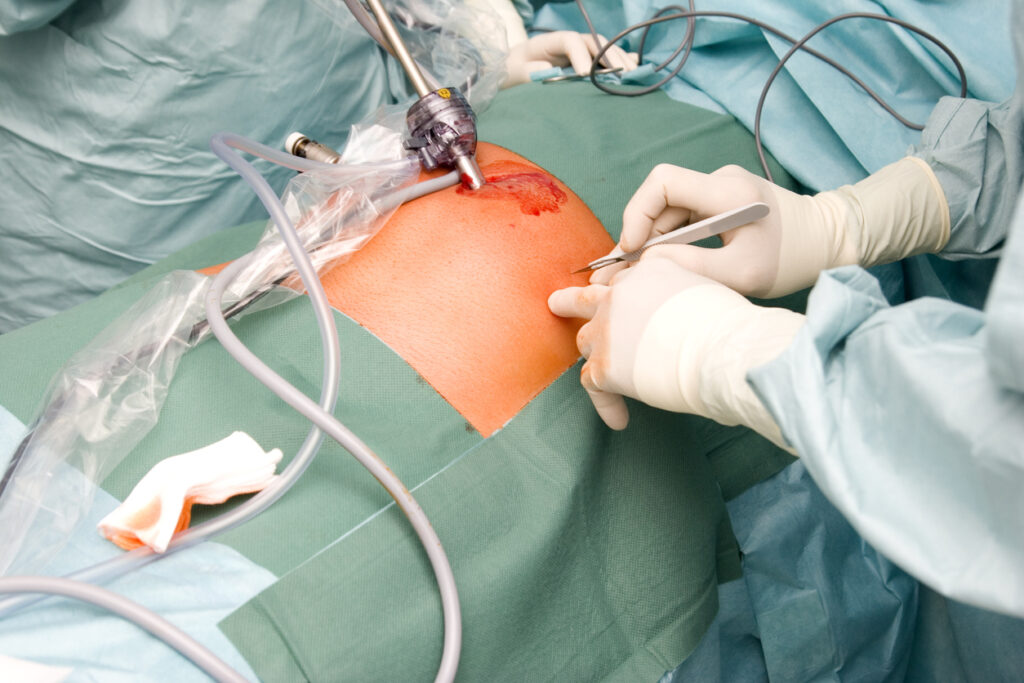
Surgical: Surgical wounds are caused by making an incision or excision, such as a laparotomy incision.
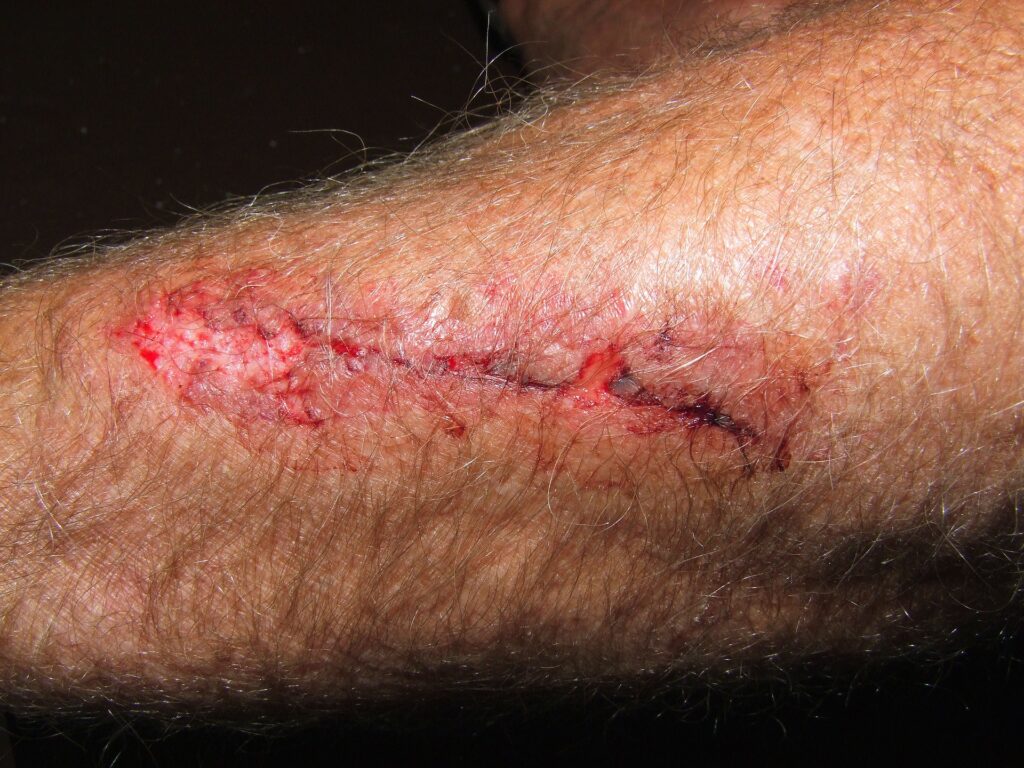
Traumatic: Traumatic wounds are skin injuries caused by mechanical, thermal, or electrical damage, such as burns.
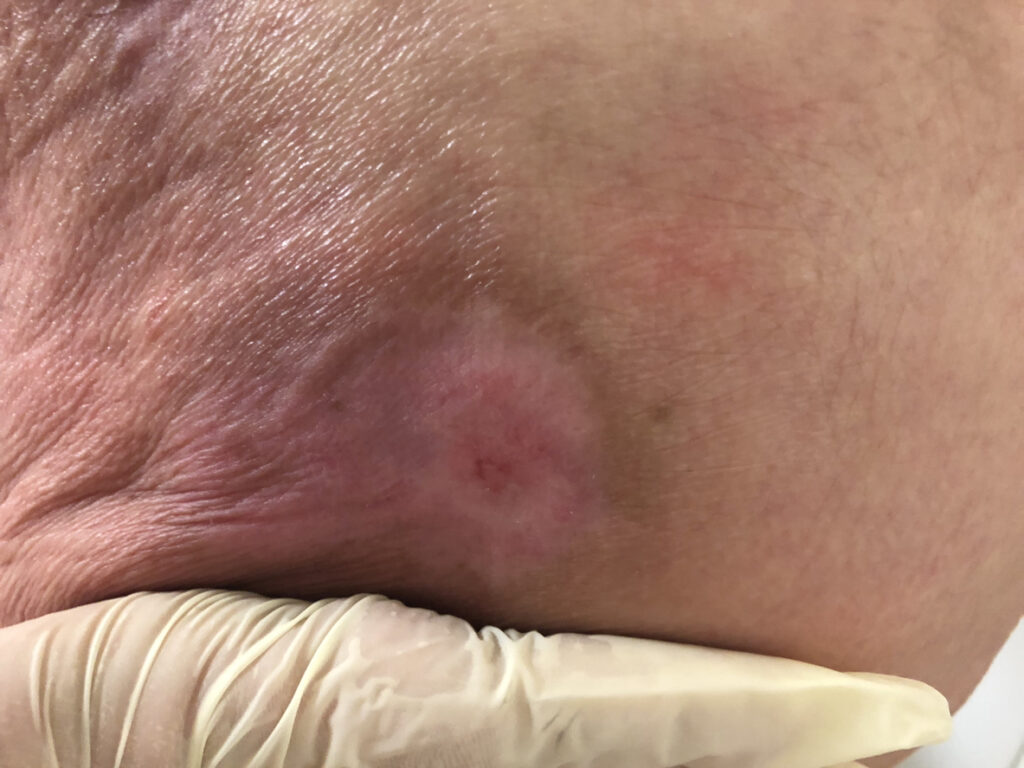
Chronic: Chronic wounds are often related to a disease process or pathophysiologic condition which can develop over time, such as a pressure sore.
(Bak, 2019)
Types of Wound Closure
Wounds can be left to heal in one of three ways: primary, secondary, or tertiary intention. Click on the links below to learn more about each.