Risk of Pressure Injury
Before arriving in the OR, the perioperative nurse needs to perform an assessment to check the patient’s pre-existing skin condition. The nurse can then assess the patient’s risk of developing a pressure injury and implement preventative interventions.
Patient positioning is a crucial factor in patient outcomes. Proper positioning requires knowledge of anatomy and physiology and familiarity with patient positioning equipment. The patient’s position is determined by the type and approach of surgery along with the surgeon’s preference.
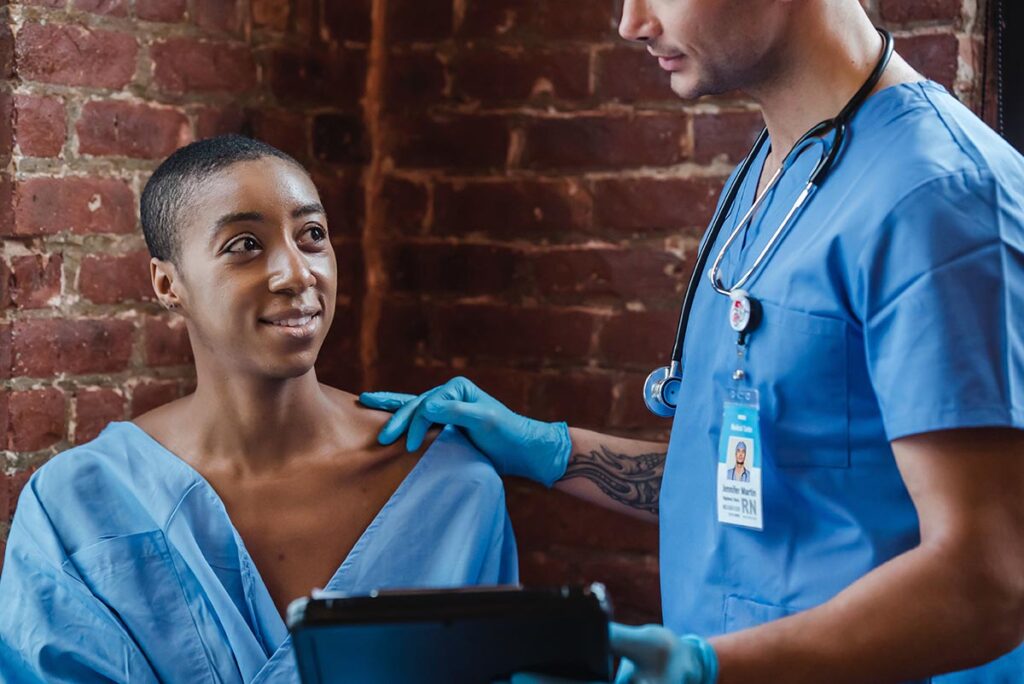
Different points on the body to see what the pre-operative risk factors are for pressure injury (select the + hotspots in the image to reveal information).
Positioning Considerations
Changes occur to the physiological and anatomical condition when positioning the patient. Factors that can affect these changes are:
- The surgical table/OR bed
- Padding
- Positioning devices used
- Type of anesthesia given
- The surgical procedure
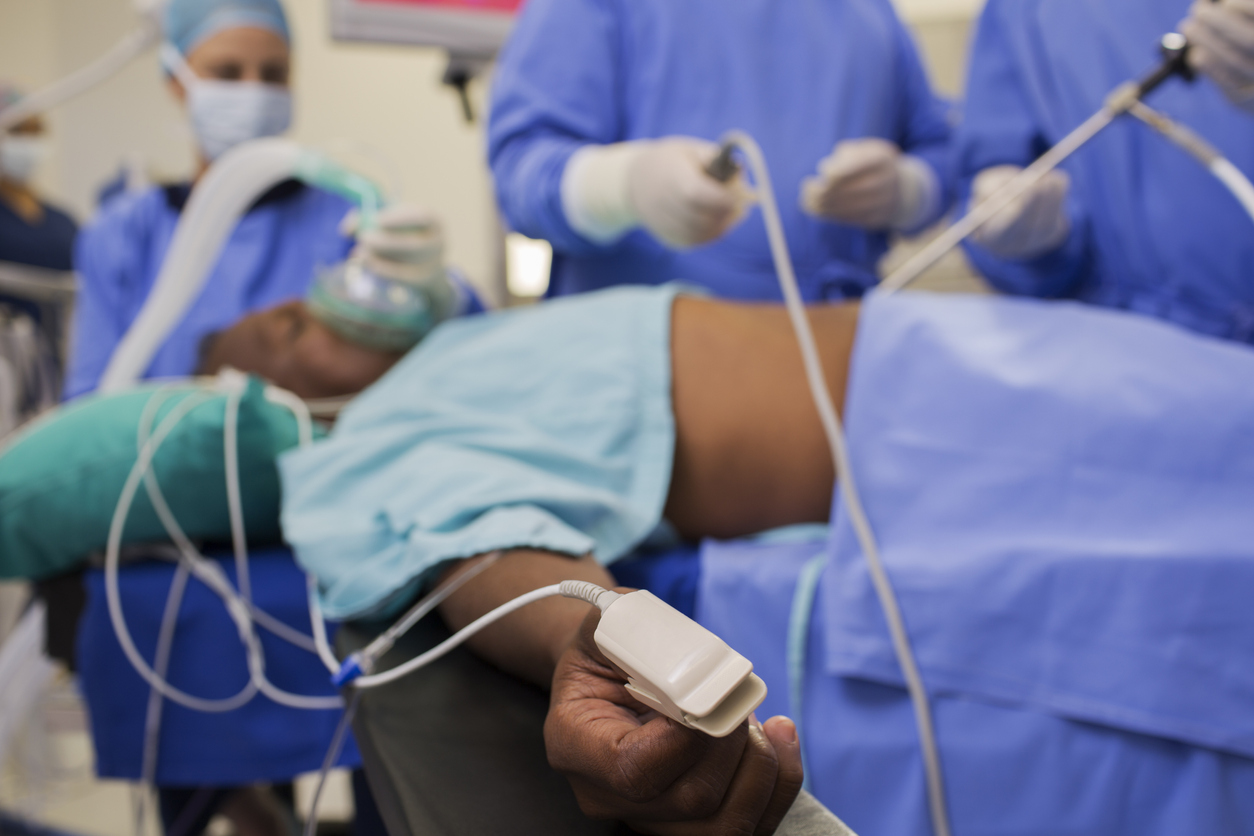
These factors impact the following systems:
- Skin and underlying tissue
- Cardiovascular system
- Musculoskeletal system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Other vulnerable areas including eyes, breasts, perineum, and digits
(ORNAC, 2021; Fawcett, 2020)
Extrinsic Risk Factors
Different physical forces can injure the skin and underlying tissues when positioning a patient and maintaining that position. Other extrinsic factors that increase the risk of a pressure injury include inadequate protection or padding, an extended length of time on the OR table, and even the use of positioning aids/devices.
Intrinsic factors can increase the patient’s risk for pressure injury as they decrease tolerance to pressure and foster skin breakdown. These factors can be pre-existing, including the patient’s age, body sizes such as obesity or a thin build, and if they smoke. Other factors include diabetes mellitus, vascular disease, peripheral vascular disease, infection, malnutrition, impaired sensory perceptions, and incontinence. Intrinsic factors can also be induced during surgery such as hypotension, certain medications such as steroids or vasopressors, low hemoglobin or hematocrit, and impaired mobility from being under general anesthesia.
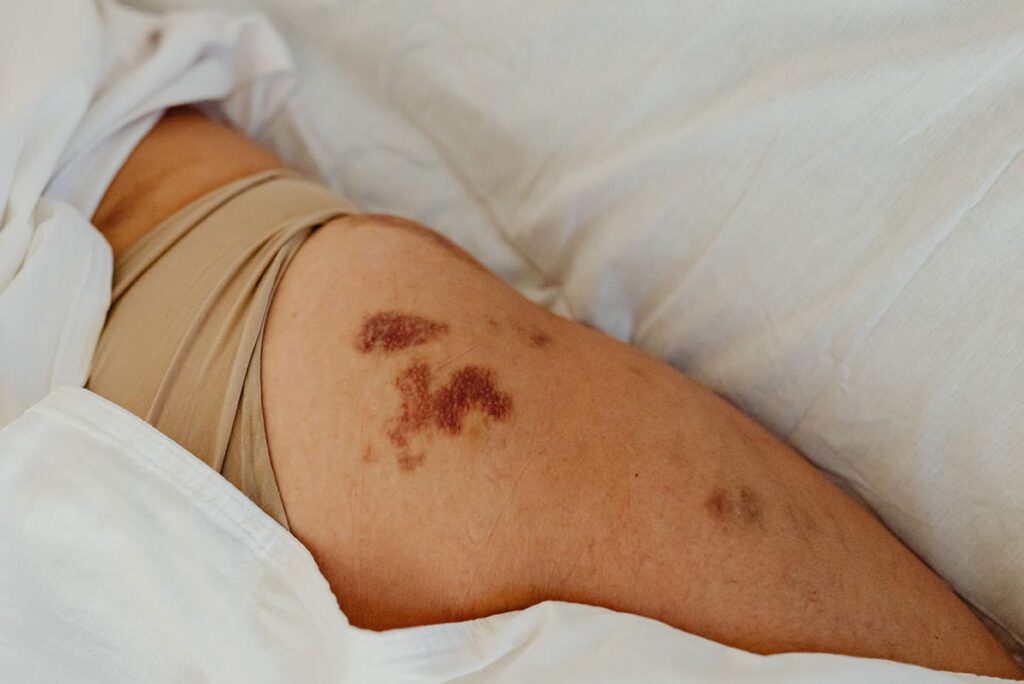
(ORNAC, 2021 & Fawcett, 2019)
Skin Risk Assessment Tool
One of the first things to prevent a patient’s skin injury is to assess their risk. There are different skin risk assessment tools, but the Munroe Pressure Ulcer Skin Assessment Scale is often used to assess the patient’s risk of skin injury during the pre-op, intraoperative, and post-op stages. Those patients identified as “at risk” can have additional interventions in place to reduce injury.
Munroe Pressure Ulcer Skin Assessment Scale for Perioperative Patient
(Fawcett, 2019)
Stages and Definition of Pressure Injury
(ORNAC,2021& Fawcett, 2019)
🧩 Practice Activity: Medical Device and Vulnerable Areas
Choose one or multiple responses to answer the question. Select “Check” when you feel confident in your answer.
Match the medical device listed into the corresponding vulnerable area associated with the device (devices may be under multiple vulnerable areas):